accuracy of hip labrum tear tests trial|A comprehensive review of hip labral tears : bulk The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only . Using steam autoclaves for sterilizing surgical instruments requires careful attention to detail and adherence to proper procedures to ensure effective sterilization and maintain instrument integrity. Here is a step-by-step .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Steris provides a table which can be used as a roadmap for your liquid autoclave runs. • Guidelines are in terms of “time” vs. “volume per flask”. • Suggested sterilization times are for .
Two novel clinical tests for the diagnosi
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); .Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In .Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found .
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .•Magnetic resonance arthrogram (MRA) is very accurate in detecting hip labral tears but costly and many tears are not clinically significant1,2. •Variable reported sensitivities and poor specificities in previously studied clinical tests-FADIR/Impingement test most commonly used4,5.
7180 chemistry analyzer
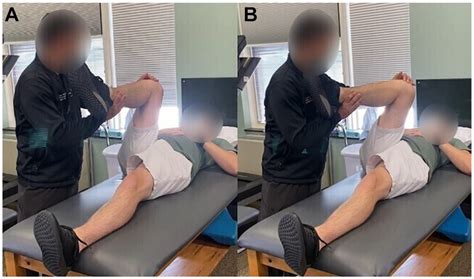
Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found that 72% of the 170 hips studied had labral tears, and 93% of these tears were in the anterior region of the labrum [76]. There are few well-studied clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip labral tears. As the differential diagnosis for hip pain is broad, accurate clinical examination is important in guiding advanced imaging and identifying patients who may benefit from surgical management.
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only screening.This study reports the diagnostic accuracy of 2 novel clinical tests for hip labral tears in a large sample of patients. The Arlington test is based on sound biomechanical principles and demonstrates a very high clinical sensitivity in detecting hip labral tears. This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
A randomized controlled trial conducted by Martin et al. recently found that patients older than 40 years with labral tears randomized to combined hip arthroscopy with physical therapy had superior patient-reported outcomes compared with patients receiving physical therapy alone. 59 Furthermore, it should be noted that, per Scott et al., both . This narrative review on mechanisms of hip pain in patients with labral tears, aimed to update rheumatologist's knowledge on: (i) clinical and imaging tools to detect labral tears; (ii) how to better identify the real source of hip/capsule pain once labral tear has been diagnosed.The sensitivity of MRIs has been reported between 25% and 67% and specificity between 67% and 79% in diagnosing labral tears. This study found that the physician was able to correctly identify labral tears more reliably than the radiologist.The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .
•Magnetic resonance arthrogram (MRA) is very accurate in detecting hip labral tears but costly and many tears are not clinically significant1,2. •Variable reported sensitivities and poor specificities in previously studied clinical tests-FADIR/Impingement test most commonly used4,5.
Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found that 72% of the 170 hips studied had labral tears, and 93% of these tears were in the anterior region of the labrum [76]. There are few well-studied clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip labral tears. As the differential diagnosis for hip pain is broad, accurate clinical examination is important in guiding advanced imaging and identifying patients who may benefit from surgical management.The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only screening.This study reports the diagnostic accuracy of 2 novel clinical tests for hip labral tears in a large sample of patients. The Arlington test is based on sound biomechanical principles and demonstrates a very high clinical sensitivity in detecting hip labral tears.
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.A randomized controlled trial conducted by Martin et al. recently found that patients older than 40 years with labral tears randomized to combined hip arthroscopy with physical therapy had superior patient-reported outcomes compared with patients receiving physical therapy alone. 59 Furthermore, it should be noted that, per Scott et al., both . This narrative review on mechanisms of hip pain in patients with labral tears, aimed to update rheumatologist's knowledge on: (i) clinical and imaging tools to detect labral tears; (ii) how to better identify the real source of hip/capsule pain once labral tear has been diagnosed.
Two Novel Clinical Tests for the Diagnos
Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip
mindray ba 88a semi-auto biochemistry analyzer
It is very important to ensure that all of the trapped air is removed from the autoclave before activation, as trapped air is a very poor medium for achieving sterility. Steam at 134 °C (273 °F) can achieve a desired level of sterility in three minutes, while achieving the same . See more
accuracy of hip labrum tear tests trial|A comprehensive review of hip labral tears